- µĄÅĶ¦ł: 168113 µ¼Ī
-

µ¢ćń½ĀÕłåń▒╗
ńżŠÕī║ńēłÕØŚ
- µłæńÜäĶĄäĶ«» ( 0)
- µłæńÜäĶ«║ÕØø ( 0)
- µłæńÜäķŚ«ńŁö ( 0)
ÕŁśµĪŻÕłåń▒╗
- 2013-12 ( 1)
- 2013-02 ( 1)
- 2013-01 ( 3)
- µø┤ÕżÜÕŁśµĪŻ...
µ£Ćµ¢░Ķ»äĶ«║
-
sydneytsao2’╝Ü
gfsńÉāµŻÆgsd
JavaĶ«ŠĶ«Īµ©ĪÕ╝ÅŌĆöŌĆöÕģŁÕż¦ÕÄ¤ÕłÖ -
µČøµČøķźŁ’╝Ü
memoryisking ÕåÖķüōÕÅ»õ╗źń£ŗń£ŗĶ┐Öń»ćµ¢ćń½Ā’╝īµ×äÕ╗║õĖĆõĖ¬ń«ĆÕŹĢńÜä ...
Javań║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĮ┐ńö©Ķ»┤µśÄ -
a492846462’╝Ü
┬Ā
Javań║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĮ┐ńö©Ķ»┤µśÄ -
sprita1’╝Ü
ĶĄäµ║ÉÕŠłÕźĮÕŠłÕ╝║Õż¦’╝īÕ»╣µź╝õĖ╗Ķ壵ŗ£õĖŁ.....
Javań║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĮ┐ńö©Ķ»┤µśÄ -
memoryisking’╝Ü
ÕÅ»õ╗źń£ŗń£ŗĶ┐Öń»ćµ¢ćń½Ā’╝īµ×äÕ╗║õĖĆõĖ¬ń«ĆÕŹĢńÜäń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā’╝Ühttp://www. ...
Javań║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĮ┐ńö©Ķ»┤µśÄ
ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā
- ÕŹÜÕ«óÕłåń▒╗’╝Ü
- JavaķØóĶ»Ģ
õĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üÕ╗║ń½ŗń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā’╝¤
┬Ā
Õ£©ÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗķĪ╣ńø«õĖŁ’╝īÕ”éµ×£Õ╗║ń½ŗńÜäń║┐ń©ŗĶ┐ćÕżÜ’╝īÕÅŹĶĆīÕÅ»ĶāĮÕ»╝Ķć┤Ķ┐ÉĶĪīķƤÕ║”Õż¦Õż¦Õćŵģó’╝īĶ┐Öµś»ńö▒õ║Äń║┐ń©ŗÕ╗║ń½ŗµēĆĶŖ▒Ķ┤╣ńÜ䵌ČķŚ┤ÕÆīĶĄäµ║ÉķāĮµ»öĶŠāÕżÜŃĆé
µēĆõ╗źµłæõ╗¼Õ£©ÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗõĖŁÕ┐ģķĪ╗ÕŠłÕźĮÕ£░µØźń«ĪńÉåń║┐ń©ŗ’╝ī Õ£©ÕŠłÕźĮÕł®ńö©ÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗĶāĮŌĆ£ÕÉīµŁźÕĘźõĮ£ŌĆØńÜäÕźĮÕżäõ╣ŗÕż¢’╝īµø┤µ£ēµĢłÕ£░µÅÉķ½śń©ŗÕ║ÅĶ┐ÉĶĪīķƤÕ║”ŃĆé
┬Ā
ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»õ╗Ćõ╣ł’╝¤
┬Ā
ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»µīćÕģʵ£ēÕø║իܵĢ░ķćÅńÜäń║┐ń©ŗń╗䵳ÉńÜäõĖĆń¦Źń╗äõ╗ČŃĆéĶ┐Öõ║øń║┐ń©ŗńö©µØźÕŠ¬ńÄ»µē¦ĶĪīÕżÜõĖ¬Õ║öńö©ķĆ╗ĶŠæŃĆé
┬Ā
µĆÄõ╣łÕ╗║ń½ŗń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā’╝¤
┬Ā
ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĖ╗Ķ”üÕīģµŗ¼4õĖ¬ķā©Õłå’╝īÕ«āõ╗¼µś»’╝Ü
1. ń║┐ń©ŗń«ĪńÉå
┬Ā
õĖ╗Ķ”üµś»ńö©µØźÕ╗║ń½ŗ’╝īÕÉ»ÕŖ©’╝īķöƵ»üÕĘźõĮ£ń║┐ń©ŗÕÆīµŖŖÕĘźõĮ£õ╗╗ÕŖĪÕŖĀÕģźÕĘźõĮ£ń║┐ń©ŗŃĆé
┬Ā
2. ÕĘźõĮ£ń║┐ń©ŗ
┬Ā
Õ«āµś»ń£¤µŁŻńÜäń║┐ń©ŗń▒╗’╝īĶ┐ÉĶĪīÕĘźõĮ£õ╗╗ÕŖĪŃĆé
┬Ā
3. ÕĘźõĮ£ķś¤ÕłŚ
┬Ā
Õ«āµś»ńö©µØźÕ░üĶŻģń║┐ń©ŗńÜäÕ«╣ÕÖ©ŃĆé
4. ÕĘźõĮ£õ╗╗ÕŖĪ
┬Ā
Õ«āµś»Õ«×ńÄ░Õ║öńö©ķĆ╗ĶŠæńÜäÕģĘõĮōń▒╗ŃĆé
┬Ā
µĄüń©ŗÕøŠ’╝Ü
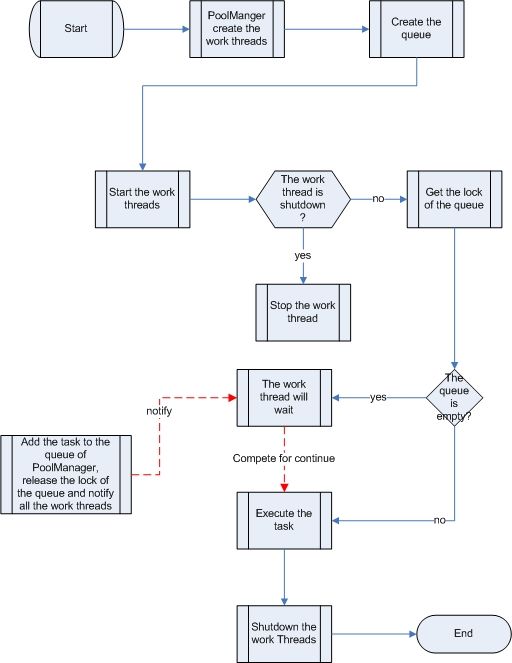
┬Ā
┬Āń║┐ń©ŗń«ĪńÉåń▒╗’╝Ü
- <SPAN┬Āstyle="COLOR:┬Ā#3366ff">import┬Ājava.util.ArrayList; ┬Ā┬Ā
- import┬Ājava.util.List; ┬Ā┬Ā
- import┬Ājava.util.Queue; ┬Ā┬Ā
- import┬Ājava.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- /** ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬ĀThreadPoolManager.java ┬Ā
- ┬Ā* ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- /** ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Āthe┬Āthread┬Āpool┬Āmanager,┬Āis┬Āresponsible┬Āfor┬Āstarting┬Āand┬Āstopping┬Āthe┬Āwork┬Āthread. ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā@author┬Ā┬Āgray ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā@version┬Ā1.0 ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- public┬Āclass┬ĀThreadPoolManager┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āprivate┬Āstatic┬Āfinal┬Āint┬ĀDEFAULT_POOL_SIZE┬Ā=┬Ā4; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āprivate┬ĀList<WorkThread>┬ĀthreadPool; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āprivate┬ĀQueue<Task>┬ĀtaskQueue; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āprivate┬Āint┬ĀpoolSize; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬ĀThreadPoolManager()┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āthis(DEFAULT_POOL_SIZE); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬ĀThreadPoolManager(int┬ĀpoolSize)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āif(poolSize┬Ā<=┬Ā0)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āthis.poolSize┬Ā=┬ĀDEFAULT_POOL_SIZE; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā}else┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āthis.poolSize┬Ā=┬ĀpoolSize; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀthreadPool┬Ā=┬Ānew┬ĀArrayList<WorkThread>(this.poolSize); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀtaskQueue┬Ā=┬Ānew┬ĀConcurrentLinkedQueue<Task>(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āstartup(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬Āvoid┬Āstartup()┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀSystem.out.println("start┬Āwork┬Āthread..."); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āsynchronized(taskQueue)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āfor(int┬Āi┬Ā=┬Ā0;┬Āi┬Ā<┬Āthis.poolSize;┬Āi++)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀWorkThread┬ĀworkThread┬Ā=┬Ānew┬ĀWorkThread(taskQueue); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀthreadPool.add(workThread); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀworkThread.start(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬Āvoid┬Āshutdown()┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀSystem.out.println("shutdown┬Āwork┬Āthread..."); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āsynchronized(taskQueue)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āfor(int┬Āi┬Ā=┬Ā0;┬Āi┬Ā<┬Āthis.poolSize;┬Āi++)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀthreadPool.get(i).shutdown(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā}┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀSystem.out.println("done..."); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬Āvoid┬ĀaddTask(Task┬Ātask)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āsynchronized(taskQueue)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀtaskQueue.add(task); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀtaskQueue.notify(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- }</SPAN>┬Ā┬Ā
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
/**
* ThreadPoolManager.java
*
*/
/**
* the thread pool manager, is responsible for starting and stopping the work thread.
*
* @author gray
* @version 1.0
*/
public class ThreadPoolManager {
private static final int DEFAULT_POOL_SIZE = 4;
private List<WorkThread> threadPool;
private Queue<Task> taskQueue;
private int poolSize;
public ThreadPoolManager() {
this(DEFAULT_POOL_SIZE);
}
public ThreadPoolManager(int poolSize) {
if(poolSize <= 0) {
this.poolSize = DEFAULT_POOL_SIZE;
}else {
this.poolSize = poolSize;
}
threadPool = new ArrayList<WorkThread>(this.poolSize);
taskQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Task>();
startup();
}
public void startup() {
System.out.println("start work thread...");
synchronized(taskQueue) {
for(int i = 0; i < this.poolSize; i++) {
WorkThread workThread = new WorkThread(taskQueue);
threadPool.add(workThread);
workThread.start();
}
}
}
public void shutdown() {
System.out.println("shutdown work thread...");
synchronized(taskQueue) {
for(int i = 0; i < this.poolSize; i++) {
threadPool.get(i).shutdown();
}
System.out.println("done...");
}
}
public void addTask(Task task) {
synchronized(taskQueue) {
taskQueue.add(task);
taskQueue.notify();
}
}
}
┬Ā
ÕĘźõĮ£ń║┐ń©ŗń▒╗’╝Ü
- <SPAN┬Āstyle="COLOR:┬Ā#3366ff">import┬Ājava.util.Queue; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- /** ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬ĀWorkThread.java ┬Ā
- ┬Ā* ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- /** ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Āthe┬Āwork┬Āthread┬Āused┬Āpull┬Āthe┬Ātask┬Āof┬Ātask┬Āqueue,┬Āand┬Āexecute┬Āit. ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā@author┬Ā┬Āgray ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā@version┬Ā1.0 ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- public┬Āclass┬ĀWorkThread┬Āextends┬ĀThread┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āprivate┬Āboolean┬Āshutdown┬Ā=┬Āfalse; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āprivate┬ĀQueue<Task>┬Āqueue; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬ĀWorkThread(Queue<Task>┬Āqueue)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āthis.queue┬Ā=┬Āqueue; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬Āvoid┬Ārun()┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āwhile(!shutdown)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ātry┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀThread.sleep(1000); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā}┬Ācatch┬Ā(InterruptedException┬Āe1)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āe1.printStackTrace(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀSystem.out.println(Thread.currentThread()┬Ā+┬Ā"┬Āis┬Ārunning..."); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āsynchronized(queue)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āif(!queue.isEmpty())┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀTask┬Ātask┬Ā=┬Āqueue.poll(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ātask.execute(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā}else┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ātry┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āqueue.wait(1000); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀSystem.out.println(Thread.currentThread()┬Ā+┬Ā"┬Āwait..."); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā}catch(InterruptedException┬Āe)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬Āvoid┬Āshutdown()┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āshutdown┬Ā=┬Ātrue; ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- }</SPAN>┬Ā┬Ā
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* WorkThread.java
*
*/
/**
* the work thread used pull the task of task queue, and execute it.
*
* @author gray
* @version 1.0
*/
public class WorkThread extends Thread {
private boolean shutdown = false;
private Queue<Task> queue;
public WorkThread(Queue<Task> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run() {
while(!shutdown) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " is running...");
synchronized(queue) {
if(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Task task = queue.poll();
task.execute();
}else {
try {
queue.wait(1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " wait...");
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
}
public void shutdown() {
shutdown = true;
}
}
┬Ā
ÕĘźõĮ£õ╗╗ÕŖĪµÄźÕÅŻ’╝Ü
┬Ā
- <SPAN┬Āstyle="COLOR:┬Ā#3366ff">/** ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬ĀTask.java ┬Ā
- ┬Ā* ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- /** ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬ĀThe┬Ātask┬Āwant┬Āto┬Āexecute. ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā@author┬Ā┬Āgray ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā@version┬Ā1.0 ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- public┬Āinterface┬ĀTask┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬Āvoid┬Āexecute(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- }</SPAN>┬Ā┬Ā
/**
* Task.java
*
*/
/**
* The task want to execute.
*
* @author gray
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface Task {
public void execute();
}
┬Ā
ÕĘźõĮ£õ╗╗ÕŖĪń▒╗’╝Ü
- <SPAN┬Āstyle="COLOR:┬Ā#3366ff">/** ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬ĀSimpleTask.java ┬Ā
- ┬Ā* ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- /** ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā@author┬Ā┬Āgray ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā@version┬Ā1.0 ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- public┬Āclass┬ĀSimpleTask┬Āimplements┬ĀTask┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā/*┬Ā(non-Javadoc) ┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā*┬Ā@see┬ĀTask#execute() ┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬Āvoid┬Āexecute()┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀSystem.out.println(Thread.currentThread()); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- }</SPAN>┬Ā┬Ā
/**
* SimpleTask.java
*
*/
/**
* @author gray
* @version 1.0
*/
public class SimpleTask implements Task {
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see Task#execute()
*/
public void execute() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
}
}
┬Ā
ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀµĄŗĶ»Ģń▒╗’╝Ü
- <SPAN┬Āstyle="COLOR:┬Ā#3366ff">/** ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬ĀThreadPoolDemo.java ┬Ā
- ┬Ā* ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- /** ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā@author┬Ā┬Āgray ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*┬Ā@version┬Ā1.0 ┬Ā
- ┬Ā*/┬Ā┬Ā
- public┬Āclass┬ĀThreadPoolDemo┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āpublic┬Āstatic┬Āvoid┬Āmain(String[]┬Āargs)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀThreadPoolManager┬ĀthreadMg┬Ā=┬Ānew┬ĀThreadPoolManager(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āfor(int┬Āi┬Ā=┬Ā0;┬Āi┬Ā<┬Ā50;┬Āi++)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀthreadMg.addTask(new┬ĀSimpleTask()); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ātry┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀThread.sleep(5000); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā}┬Ācatch┬Ā(InterruptedException┬Āe)┬Ā{ ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Āe.printStackTrace(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā} ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬ĀthreadMg.shutdown(); ┬Ā┬Ā
- ┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā}┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā┬Ā
- }</SPAN>┬Ā┬Ā
- 2012-07-30 15:50
- µĄÅĶ¦ł 985
- Ķ»äĶ«║(0)
- Õłåń▒╗:õ╝üõĖܵ×ȵ×ä
- µ¤źń£ŗµø┤ÕżÜ
ÕÅæĶĪ©Ķ»äĶ«║
-
ķŚ«ķóśÕłŚĶĪ©
2012-08-15 22:01 8701.Õ”éõĮĢķ¬īĶ»üxmlµ¢ćõ╗ȵś»ÕÉ”ń¼”ÕÉłĶ¦äĶīā 2.sqlÕĖĖńö©µōŹõĮ£Õ╗║ÕŁśÕé© ... -
ŃĆÉJDBCŃĆæjavaõĖŁÕĖĖĶ¦üõĖēń¦Źµ│©Õåīķ®▒ÕŖ©µ¢╣Õ╝ŵ»öĶŠā
2012-08-08 09:26 10981.DriverManager.registerDriver( ... -
µÄÆÕ║ÅķāĮµ£ēÕō¬ÕćĀń¦Źµ¢╣µ│Ģ
2012-08-03 08:49 1517µÄÆÕ║ŵ¢╣µ│ĢõĖĆĶł¼ķāĮÕ░▒ķéŻÕćĀń ... -
JavaիܵŚČÕÖ©
2012-08-02 14:28 0Ķ»ĘĶ»┤Ķ»┤õĮĀÕ»╣JavaիܵŚČÕÖ©ńÜäĶ«żĶ»å’╝īÕ░ØĶ»ĢÕåÖõĖĆõĖ¬õŠŗÕŁÉµØźĶ»┤µśÄŃĆé ńŁö’╝ÜÕ£© ... -
ń╝¢ÕåÖõĖĆõĖ¬ń©ŗÕ║Å’╝īÕ░åd:\javańø«ÕĮĢõĖŗńÜäµēƵ£ē.javaµ¢ćõ╗ČÕżŹÕłČÕł░d:\jadńø«ÕĮĢõĖŗ’╝īÕ╣ČÕ░åÕĤµØźµ¢ćõ╗ČńÜäµē®Õ▒ĢÕÉŹõ╗Ä.javaµö╣õĖ║.jad
2012-08-02 11:54 2903ń╝¢ÕåÖõĖĆõĖ¬ń©ŗÕ║Å’╝īÕ░åd:\javańø«ÕĮĢõĖŗńÜäµēƵ£ē.javaµ¢ćõ╗ČÕżŹÕłČÕł░ ... -
javaõĖŁµĄüńÜäĶ»”Ķ¦Ż
2012-08-01 16:50 1052javaõĖŁµĄüńÜäĶ»”Ķ¦Ż ÕŹÜÕ«óÕłåń▒╗’╝Ü j2ee ... -
Õ”éõĮĢÕżäńÉåÕż¦µĢ░µŹ«ķćÅńÜ䵤źĶ»ó
2012-07-31 14:38 3444J2EEń╗╝ÕÉł’╝ÜÕ”éõĮĢÕżäńÉåÕż¦µĢ░ ... -
Õż¦µĢ░µŹ«ķćÅÕżäńÉå
2012-07-31 10:59 914Õż¦µĢ░µŹ«ķćÅÕżäńÉå’╝łõĖĆ’╝ē ┬Ā ┬Ā Õż¦µĢ░µŹ«ķćÅńÜäķŚ«ķ󜵜»ÕŠłÕżÜķØóĶ»Ģń¼öĶ»Ģ ... -
õĖēķüōķØóĶ»Ģķóś
2012-07-31 10:01 1085[Ķ«©Ķ«║]┬Āõ╗ŖÕż®ÕÄ╗ķØóĶ»Ģõ║å’╝īµ£ēõĖēõĖ¬ķóśńø«ķŚ«ÕĆƵłæõ║å’╝īÕåÖÕć║µØźÕż¦Õ«ČÕüÜÕüÜ’╝ü ... -
Õ«×ńÄ░õ╗ĵ¢ćõ╗ČõĖŁõĖƵ¼ĪĶ»╗Õć║õĖĆõĖ¬ÕŁŚń¼”ńÜäµōŹõĮ£,javaÕ«×ńÄ░õ╗ĵ¢ćõ╗ČõĖŁõĖƵ¼ĪĶ»╗Õć║õĖĆõĖ¬ÕŁŚń¼”ńÜäµōŹõĮ£
2012-07-30 16:41 0Õ«×ńÄ░õ╗ĵ¢ćõ╗ČõĖŁõĖƵ¼ĪĶ»╗Õć║õĖĆõĖ¬ÕŁŚń¼”ńÜäµōŹõĮ£,javaÕ«×ńÄ░õ╗ĵ¢ćõ╗ČõĖŁ ... -
Javań║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĮ┐ńö©Ķ»┤µśÄ
2012-07-30 16:35 59902Javań║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĮ┐ńö©Ķ»┤µśÄ õĖĆ ń«Ćõ╗ŗ ń║┐ń©ŗńÜäõĮ┐ńö©Õ£©javaõĖŁÕŹĀ ... -
õĖĆõĖ¬ń«ĆÕŹĢńÜäń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā
2012-07-30 15:55 1052import┬Ājava.util.LinkedList; ┬Ā ... -
JavaÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗ:ń▒╗ThreadPoolExecutorĶ»”Ķ¦Ż
2012-07-30 15:04 1412JavaÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗ:ń▒╗ThreadPoolExecutor ... -
Javań©ŗÕ║ÅÕæśķØóĶ»ĢõĖŁńÜäÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗķŚ«ķóś
2012-07-30 14:42 621ÕŠłÕżÜµĀĖÕ┐ā Java ķØóĶ»ĢķóśµØźµ ...








ńøĖÕģ│µÄ©ĶŹÉ
ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»õĖĆń¦ŹÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗÕżäńÉåÕĮóÕ╝Å’╝īķĆÜĶ┐ćķóäÕģłÕłøÕ╗║õĖĆիܵĢ░ķćÅńÜäń║┐ń©ŗÕ╣Čń«ĪńÉåÕ«āõ╗¼’╝īõ╗źµÅÉķ½śń│╗ń╗¤ńÜäµĢłńÄćÕÆīÕōŹÕ║öµĆ¦ŃĆéÕ£©Ķ«Īń«Śµ£║ń¦æÕŁ”õĖŁ’╝īńē╣Õł½µś»Õ£©ĶĮ»õ╗ČÕ╝ĆÕÅæķóåÕ¤¤’╝īń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»µōŹõĮ£ń│╗ń╗¤µł¢ĶĆģń╝¢ń©ŗĶ»ŁĶ©ĆõĖŁńÜäõĖĆń¦ŹĶĄäµ║Éń«ĪńÉåµŖƵ£»ŃĆéÕ«āÕģüĶ«Ėń©ŗÕ║ÅķóäÕģłÕÉ»ÕŖ©õĖĆ...
corePoolSize’╝ܵĀĖÕ┐āµ▒ĀńÜäÕż¦Õ░Å’╝īÕ£©ÕłøÕ╗║õ║åń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕÉÄ’╝īń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĖŁńÜäń║┐ń©ŗµĢ░õĖ║0’╝īÕĮōµ£ēõ╗╗ÕŖĪµØźõ╣ŗÕÉÄ’╝īÕ░▒õ╝ÜÕłøÕ╗║õĖĆõĖ¬ń║┐ń©ŗÕÄ╗µē¦ĶĪīõ╗╗ÕŖĪ’╝īÕĮōń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĖŁńÜäń║┐ń©ŗµĢ░ńø«ĶŠŠÕł░corePoolSizeÕÉÄ’╝īÕ░▒õ╝ܵŖŖÕł░ĶŠŠńÜäõ╗╗ÕŖĪµöŠÕł░ń╝ōÕŁśķś¤ÕłŚÕĮōõĖŁ; ...
ķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āķś╗ÕĪ×ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā...
õĖĆŃĆüĶ”üÕ«×ńÄ░ķ½śµĢłńÜäń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā’╝īÕÅ»õ╗źĶĆāĶÖæõ╗źõĖŗÕćĀńé╣ õ║īŃĆüÕ«×ńÄ░ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕÅ»õ╗źµīēńģ¦õ╗źõĖŗµŁźķ¬żĶ┐øĶĪī õĖēŃĆüń«ĆÕŹĢńÜäC++ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āõ╗ŻńĀüńż║õŠŗ ÕøøŃĆü Õ¤║õ║Äboostń╝¢ÕåÖńÜäµ║ÉńĀüÕ║ō - ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā 4.1 Õ¤║õ║Äboostń╝¢ÕåÖńÜäµ║ÉńĀüÕ║ōÕ£░ÕØĆ 4.2 boostń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀńÜäÕģłĶ┐øÕģłÕć║ŃĆü...
### ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕĤńÉåÕÅŖÕłøÕ╗║’╝łC++Õ«×ńÄ░’╝ē #### õĖĆŃĆüń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀńÜäķćŹĶ”üµĆ¦ Õ£©ńÄ░õ╗ŻĶ«Īń«ŚńÄ»ÕóāõĖŁ’╝īńĮæń╗£µ£ŹÕŖĪÕÖ©ķØóõĖ┤ńØĆÕżäńÉåÕż¦ķćÅÕ╣ČÕÅæĶ»Ęµ▒éńÜäµīæµłś’╝īÕģČõĖŁÕīģµŗ¼õĮåõĖŹķÖÉõ║ÄWebµ£ŹÕŖĪÕÖ©ŃĆüńöĄÕŁÉķé«õ╗ȵ£ŹÕŖĪÕÖ©ÕÆīµĢ░µŹ«Õ║ōµ£ŹÕŖĪÕÖ©ŃĆéĶ┐Öń▒╗µ£ŹÕŖĪÕÖ©ķĆÜÕĖĖķ£ĆĶ”üÕ£©ń¤ŁµŚČķŚ┤...
javań║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĮ┐ńö©ÕÉÄÕł░Õ║ĢĶ”üÕģ│ķŚŁÕÉŚ javań║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»õĖĆń¦Źķ½śµĢłńÜäÕ╣ČÕÅæń╝¢ń©ŗµŖƵ£»’╝īÕÅ»õ╗źÕĖ«ÕŖ®Õ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģµø┤ÕźĮÕ£░ń«ĪńÉåń║┐ń©ŗĶĄäµ║É’╝īµÅÉķ½śń│╗ń╗¤ńÜäµĆ¦ĶāĮÕÆīÕÅ»ķØĀµĆ¦ŃĆéńäČĶĆī’╝īÕ£©õĮ┐ńö©javań║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀµŚČ’╝īõĖĆõĖ¬ÕĖĖĶ¦üńÜäķŚ«ķ󜵜»’╝ÜõĮ┐ńö©Õ«īń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕÉÄÕł░Õ║ĢĶ”üõĖŹĶ”üÕģ│ķŚŁ’╝¤...
µ¢ćń½ĀķĆÜĶ┐ćÕ«×õŠŗÕ▒Ģńż║õ║åÕ”éõĮĢÕłøÕ╗║õĖĆõĖ¬Õģ©Õ▒Ćń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āń▒╗’╝īĶ»źń▒╗õĖŁÕ░üĶŻģõ║åń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕ»╣Ķ▒Ī’╝īÕ╣ȵÅÉõŠøõ║åÕÉæń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀµÅÉõ║żõ╗╗ÕŖĪŃĆüµŻĆµ¤źõ╗╗ÕŖĪµś»Õɔգ©Ķ┐ÉĶĪīńŁēµ¢╣µ│ĢŃĆéÕģ©Õ▒Ćń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀńÜäńö¤ÕæĮÕ橵£¤õĖÄDjangoõĖ╗ń║┐ń©ŗńÜäńö¤ÕæĮÕ橵£¤õĖĆĶć┤’╝īńĪ«õ┐Øõ║åń║┐ń©ŗĶĄäµ║ÉńÜäÕÉłńÉåķćŖµöŠŃĆé 5....
ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»ÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗń╝¢ń©ŗõĖŁńÜäõĖĆõĖ¬ķćŹĶ”üµ”éÕ┐Ą’╝īÕ«āµś»õĖĆń¦Źń║┐ń©ŗõĮ┐ńö©µ©ĪÕ╝Å’╝īķĆÜĶ┐ćķóäÕģłÕłøÕ╗║õĖĆń╗äń║┐ń©ŗÕ╣Čń╗┤µŖżõĖĆõĖ¬ń║┐ń©ŗķøåÕÉłµØźÕżäńÉåÕ╣ČÕÅæõ╗╗ÕŖĪŃĆéÕ£©WindowsµōŹõĮ£ń│╗ń╗¤õĖŁ’╝īÕåģÕ╗║ńÜäń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀAPI’╝łThread Pool API’╝ēµÅÉõŠøõ║åķ½śµĢłõĖöńüĄµ┤╗ńÜäń║┐ń©ŗń«ĪńÉåµ£║ÕłČ’╝ī...
ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»õĖĆń¦ŹÕ£©ÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗń╝¢ń©ŗõĖŁķØ×ÕĖĖķćŹĶ”üńÜäµ”éÕ┐Ą’╝īÕ«āĶāĮµ£ēµĢłÕ£░ń«ĪńÉåÕÆīĶ░āÕ║”ń│╗ń╗¤õĖŁńÜäń║┐ń©ŗĶĄäµ║É’╝īõ╗ÄĶĆīµÅÉķ½śń│╗ń╗¤ńÜäµĢłńÄćÕÆīÕōŹÕ║öķƤÕ║”ŃĆéÕ£©Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬ń«ĆÕŹĢńÜäń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕ«×ńÄ░õĖŁ’╝īµłæõ╗¼ÕÅ»õ╗źķĆÜĶ┐ć`pthread_pool.cpp`ŃĆü`MainFunctionForTest.cpp`ŃĆü`...
Õ£©ń╝¢ń©ŗķóåÕ¤¤’╝īń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»õĖĆń¦ŹÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗÕżäńÉåÕĮóÕ╝Å’╝īÕżäńÉåĶ┐ćń©ŗõĖŁÕ░åõ╗╗ÕŖĪµĘ╗ÕŖĀÕł░ķś¤ÕłŚ’╝īńäČÕÉÄÕ£©ÕłøÕ╗║ń║┐ń©ŗÕÉÄĶć¬ÕŖ©ÕÉ»ÕŖ©Ķ┐Öõ║øõ╗╗ÕŖĪŃĆéń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕ£©C++õĖŁµś»µÅÉķ½śń©ŗÕ║ŵĢłńÄćÕÆīĶĄäµ║Éń«ĪńÉåńÜäķćŹĶ”üÕĘźÕģĘ’╝īÕ░żÕģČÕ£©ÕżäńÉåÕż¦ķćÅÕ╣ČÕÅæµōŹõĮ£µŚČŃĆéµ£¼µ¢ćÕ░åµĘ▒ÕģźµÄóĶ«©VC++õĖŁ...
Java8Õ╣ČĶĪīµĄüõĖŁĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀµōŹõĮ£ńż║õŠŗ Java8Õ╣ČĶĪīµĄüõĖŁĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀµōŹõĮ£ńż║õŠŗõĖ╗Ķ”üõ╗ŗń╗Źõ║åJava8Õ╣ČĶĪīµĄüõĖŁĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀµōŹõĮ£’╝īń╗ōÕÉłÕ«×õŠŗÕĮóÕ╝ÅÕłåµ×Éõ║åÕ╣ČĶĪīµĄüńÜäńøĖÕģ│µ”éÕ┐ĄŃĆüÕ«Üõ╣ēÕÅŖĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀńÜäńøĖÕģ│µōŹõĮ£µŖĆÕʦŃĆé 1. µ”éĶ¦ł Java8Õ╝ĢÕģźõ║å...
Linux ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕłøÕ╗║ C Õ«×ńÄ░ ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»õĖĆń¦ŹÕĖĖńö©ńÜäÕ╣ČÕÅæń╝¢ń©ŗµŖƵ£»’╝īÕ«āÕÅ»õ╗źµÅÉķ½śÕ║öńö©ń©ŗÕ║ÅńÜäµĆ¦ĶāĮÕÆīÕōŹÕ║öķƤÕ║”ŃĆéÕ£© Linux ń│╗ń╗¤õĖŁ’╝īõĮ┐ńö© C Ķ»ŁĶ©ĆÕłøÕ╗║ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕÅ»õ╗źÕ«×ńÄ░ķ½śµĢłńÜäÕ╣ČÕÅæÕżäńÉåŃĆé õ╗Ćõ╣łµŚČÕĆÖķ£ĆĶ”üÕłøÕ╗║ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕæó’╝¤ń«ĆÕŹĢńÜäĶ»┤’╝īÕ”éµ×£õĖĆ...
DELPHIńÜäń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā’╝łThreadPool’╝ēµś»õĖĆń¦Źķ½śµĢłń«ĪńÉåÕ╣ČÕÅæõ╗╗ÕŖĪńÜäµŖƵ£»’╝īÕ«āÕģüĶ«Ėń©ŗÕ║ÅÕ£©ķ£ĆĶ”üµŚČÕłøÕ╗║ń║┐ń©ŗ’╝īĶĆīõĖŹµś»µ»Åµ¼Īķ£ĆĶ”üµē¦ĶĪīõ╗╗ÕŖĪµŚČķāĮµēŗÕŖ©ÕłøÕ╗║ŃĆéń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀķĆÜĶ┐ćķóäÕģłÕłøÕ╗║õĖĆń╗äń║┐ń©ŗ’╝īńäČÕÉĵĀ╣µŹ«ķ£ĆĶ”üÕłåķģŹõ╗╗ÕŖĪ’╝īÕćÅÕ░æõ║åń║┐ń©ŗÕłøÕ╗║ÕÆīķöƵ»üńÜäÕ╝ĆķöĆ’╝ī...
µ£¼ń»ćµ¢ćń½ĀÕ░åķćŹńé╣µÄóĶ«©õĖżń¦Źń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕ«×ńÄ░’╝Üń▓Šµśōµ©ĪÕØŚń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕÆīķ▒╝Õł║µ©ĪÕØŚń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā’╝īÕ╣ČķĆÜĶ┐ćµ║ÉńĀüÕłåµ×ÉµØźÕ▒Ģńż║Õ«āõ╗¼ńÜäńē╣ńé╣ÕÆīńö©µ│ĢŃĆé ķ”¢Õģł’╝īń▓Šµśōµ©ĪÕØŚ’╝łSanYe Module’╝ēµś»ńö▒õĖŁÕøĮń©ŗÕ║ÅÕæśSanYeÕ╝ĆÕÅæńÜäõĖĆń│╗ÕłŚÕ╝Ƶ║ɵ©ĪÕØŚ’╝īÕģČõĖŁÕīģÕɽõ║åń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀńÜäÕ«×ńÄ░...
Õ£©Linuxń│╗ń╗¤õĖŁ’╝īń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»õĖĆń¦Źķ½śµĢłńÜäĶ┐øń©ŗń«ĪńÉåµ¢╣Õ╝Å’╝īÕ«āÕģüĶ«ĖÕżÜõĖ¬õ╗╗ÕŖĪÕ╣ČĶĪīµē¦ĶĪī’╝īÕÉīµŚČķÖÉÕłČõ║åń│╗ń╗¤õĖŁÕ╣ČÕÅæń║┐ń©ŗńÜäµĢ░ķćÅ’╝īõ╗źõ╝śÕī¢ĶĄäµ║ÉÕłåķģŹÕÆīĶ░āÕ║”ŃĆéµ£¼ķĪ╣ńø«Õ«×ńÄ░õ║åÕł®ńö©ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀĶ┐øĶĪīńø«ÕĮĢµŗĘĶ┤ØńÜäÕŖ¤ĶāĮ’╝īĶ┐ÖµČēÕÅŖÕł░ÕżÜõĖ¬ķćŹĶ”üńÜäń╝¢ń©ŗµ”éÕ┐ĄÕÆīµŖƵ£»...
ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»õĖĆń¦Źõ╝śÕī¢ĶĄäµ║Éń«ĪńÉåńÜäµ£║ÕłČ’╝īķĆÜĶ┐ćķóäÕģłÕłøÕ╗║Õ╣Čń╗┤µŖżõĖĆń╗äÕÅ»ķćŹńö©ńÜäń║┐ń©ŗ’╝īķü┐ÕģŹķóæń╣üÕ£░ÕłøÕ╗║ÕÆīķöƵ»üń║┐ń©ŗÕĖ”µØźńÜäµĆ¦ĶāĮÕ╝ĆķöĆŃĆéÕ£©JavaŃĆüC++ńŁēń╝¢ń©ŗĶ»ŁĶ©ĆõĖŁ’╝īń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀÕ╣┐µ│øÕ║öńö©õ║ÄÕ╣ČÕÅæÕżäńÉå’╝īµÅÉķ½śń│╗ń╗¤µĢłńÄć’╝īķÖŹõĮÄń│╗ń╗¤ńÜäĶĄäµ║ɵȳĶĆŚŃĆéµ£¼ķĪ╣ńø«...
õĖĆŃĆüń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā 1ŃĆüõĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łķ£ĆĶ”üõĮ┐ńö©ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā 1.1 ÕłøÕ╗║/ķöƵ»üń║┐ń©ŗõ╝┤ķÜÅńØĆń│╗ń╗¤Õ╝ĆķöĆ’╝īĶ┐ćõ║Äķóæń╣üńÜäÕłøÕ╗║/ķöƵ»üń║┐ń©ŗ’╝īõ╝ÜÕŠłÕż¦ń©ŗÕ║”õĖŖÕĮ▒ÕōŹÕżäńÉåµĢłńÄćŃĆé Ķ«░ÕłøÕ╗║ń║┐ń©ŗµČłĶĆŚµŚČķŚ┤T1’╝īµē¦ĶĪīõ╗╗ÕŖĪµČłĶĆŚµŚČķŚ┤T2’╝īķöƵ»üń║┐ń©ŗµČłĶĆŚµŚČķŚ┤T3’╝īÕ”éµ×£T1+T3>T2’╝īķéŻ...
ń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āń«ĪńÉåÕÆīÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗõĖŖõ╝Āµś»Õ╣ČÕÅæń╝¢ń©ŗõĖŁńÜäõĖĆõĖ¬ķćŹĶ”üÕ«×ĶĘĄ’╝īńē╣Õł½µś»Õ£©Õż¦µĢ░µŹ«õ╝ĀĶŠōÕÆīńĮæń╗£µ£ŹÕŖĪõĖŁŃĆéÕ£©JavańŁēń╝¢ń©ŗĶ»ŁĶ©ĆõĖŁ’╝īń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀķĆÜĶ┐ćµ£ēµĢłÕ£░ń«ĪńÉåÕÆīÕżŹńö©ń║┐ń©ŗĶĄäµ║É’╝īķü┐ÕģŹõ║åķóæń╣üÕłøÕ╗║ÕÆīķöƵ»üń║┐ń©ŗÕĖ”µØźńÜäÕ╝ĆķöĆ’╝īµÅÉÕŹćõ║åń│╗ń╗¤µĆ¦ĶāĮŃĆéõĖŗķØóÕ░åĶ»”ń╗å...
Õ£©TomcatńÜäķģŹńĮ«ÕÆīµĆ¦ĶāĮõ╝śÕī¢õĖŁ’╝īõ║åĶ¦ŻÕ”éõĮĢĶ«ŠńĮ«Ķ┐׵ğµĢ░ÕÆīń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Āµś»Ķć│Õģ│ķćŹĶ”üńÜäŃĆé ķ”¢Õģł’╝īConnectorµīēńģ¦ÕżäńÉåĶ┐׵ğńÜäµ¢╣Õ╝ÅÕÅ»õ╗źÕłåõĖ║õĖŹÕÉīńÜäÕŹÅĶ««ń▒╗Õ×ŗ’╝īÕīģµŗ¼BIO’╝łķś╗ÕĪ×IO’╝ēŃĆüNIO’╝łķØ×ķś╗ÕĪ×IO’╝ēŃĆüAPR’╝łApache Portable Runtime’╝ēŃĆéBIO...
Õ£©C#ń╝¢ń©ŗõĖŁ’╝īń║┐ń©ŗµ▒Ā’╝łThreadPool’╝ēµś»õĖĆń¦Źķ½śµĢłńÜäń║┐ń©ŗń«ĪńÉåµ£║ÕłČ’╝īÕ«āÕģüĶ«ĖÕ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģÕłøÕ╗║Õ╣Čń«ĪńÉåÕżÜõĖ¬ń║┐ń©ŗ’╝īĶĆīµŚĀķ£Ćńø┤µÄźµōŹõĮ£ń║┐ń©ŗÕ»╣Ķ▒ĪŃĆéń║┐ń©ŗµ▒ĀõĖŁńÜäń║┐ń©ŗÕÅ»õ╗źÕżŹńö©’╝īÕćÅÕ░æõ║åÕłøÕ╗║ÕÆīķöƵ»üń║┐ń©ŗńÜäÕ╝ĆķöĆŃĆéÕĮōµłæõ╗¼ķ£ĆĶ”üµē¦ĶĪīÕż¦ķćÅń¤Łńö¤ÕæĮÕ橵£¤ńÜäõ╗╗ÕŖĪ...