- 浏览: 142309 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 深圳
-

文章分类
最新评论
-
yizishou:
很详细,不错
Oracle 索引的五种类型 -
xinyoulinglei:
学习了 不错的文章 要是里面在有一些案例的说明就更好了
oracle,Cannot SET AUTOTRACE解决问题 -
xiaolobster:
我想问一下 上面这个函数,如果字符串超长了如何调整?拼成的字 ...
拼字符串 将多行拼成一行 -
DataBird:
非常感谢你无私的奉献,这个函数太棒了!!!
拿来可以直接用。
...
拼字符串 将多行拼成一行
Oracle Optimizer CBO RBO http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/archive/2010/08/19/5824886.aspx Oracle 索引 详解 http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/archive/2010/03/05/5347098.aspx Oracle Explain Plan http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/archive/2010/08/20/5827245.aspx 根据索引的类型与where限制条件的不同,有4种类型的Oracle索引扫描: (1) 索引唯一扫描(index unique scan) (2) 索引范围扫描(index range scan) (3) 索引全扫描(index full scan) (4) 索引快速扫描(index fast full scan) (5) 索引跳跃扫描(INDEX SKIP SCAN) 一. 索引唯一扫描(index unique scan) 通过唯一索引查找一个数值经常返回单个ROWID。如果该唯一索引有多个列组成(即组合索引),则至少要有组合索引的引导列参与到该查询中,如创建一个索引:create index idx_test on emp(ename, deptno, loc)。则select ename from emp where ename = ‘JACK’ and deptno = ‘DEV’语句可以使用该索引。如果该语句只返回一行,则存取方法称为索引唯一扫描。而select ename from emp where deptno = ‘DEV’语句则不会使用该索引,因为where子句种没有引导列。如果存在UNIQUE 或PRIMARY KEY 约束(它保证了语句只存取单行)的话,Oracle经常实现唯一性扫描。 如: SQL> set autot traceonly exp; -- 只显示执行计划 SQL> select * from scott.emp t where t.empno=10; 执行计划 ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 2949544139 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 38 | 1 (0)| 00:0 | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 38 | 1 (0)| 00:0 |* 2 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | PK_EMP | 1 | | 0 (0)| 00:0 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 2 - access("T"."EMPNO"=10) 二.索引范围扫描(index range scan) 使用一个索引存取多行数据,同上面一样,如果索引是组合索引,而且select ename from emp where ename = ‘JACK’ and deptno = ‘DEV’语句返回多行数据,虽然该语句还是使用该组合索引进行查询,可此时的存取方法称为索引范围扫描。 在唯一索引上使用索引范围扫描的典型情况下是在谓词(where限制条件)中使用了范围操作符(如>、<、<>、>=、<=、between) 使用索引范围扫描的例子: SQL> select empno,ename from scott.emp where empno > 7876 order by empno; 执行计划 ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 169057108 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 10 | 2 (0)| 00:0 | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 1 | 10 | 2 (0)| 00:0 |* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | PK_EMP | 1 | | 1 (0)| 00:0 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 2 - access("EMPNO">7876) 在非唯一索引上,谓词可能返回多行数据,所以在非唯一索引上都使用索引范围扫描。 使用index rang scan的3种情况: (a) 在唯一索引列上使用了range操作符(> < <> >= <= between)。 三.索引全扫描(index full scan) 与全表扫描对应,也有相应的全Oracle索引扫描。在某些情况下,可能进行全Oracle索引扫描而不是范围扫描,需要注意的是全Oracle索引扫描只在CBO模式下才有效。 CBO根据统计数值得知进行全Oracle索引扫描比进行全表扫描更有效时,才进行全Oracle索引扫描,而且此时查询出的数据都必须从索引中可以直接得到。 全Oracle索引扫描的例子: SQL> create index big_emp on scott.emp(empno,ename); 索引已创建。 SQL> select empno, ename from scott.emp order by empno,ename; 执行计划 ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 322359667 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 14 | 140 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | | 1 | INDEX FULL SCAN | BIG_EMP | 14 | 140 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 四. 索引快速扫描(index fast full scan) 扫描索引中的所有的数据块,与 index full scan很类似,但是一个显著的区别就是它不对查询出的数据进行排序,即数据不是以排序顺序被返回。在这种存取方法中,可以使用多块读功能,也可以使用并行读入,以便获得最大吞吐量与缩短执行时间。 索引快速扫描的例子: SQL> select /*+ index_ffs(dave index_dave) */ id from dave where id>0; 执行计划 ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 674200218 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 8 | 24 | 2 (0)| 00:00:0 |* 1 | INDEX FAST FULL SCAN| INDEX_DAVE | 8 | 24 | 2 (0)| 00:00:0 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 1 - filter("ID">0) 为了实现这个效果,折腾了半天,最终还是用hint来了. Oracle Hint http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/archive/2010/03/05/5347098.aspx 五. 索引跳跃扫描(INDEX SKIP SCAN) INDEX SKIP SCAN,发生在多个列建立的复合索引上,如果SQL中谓词条件只包含索引中的部分列,并且这些列不是建立索引时的第一列时,就可能发生INDEX SKIP SCAN。这里SKIP的意思是因为查询条件没有第一列或前面几列,被忽略了。 Oracle 10g的文档如下: Index skip scans improve index scans by nonprefix columns. Often, scanning index blocks is faster than scanning table data blocks. Skip scanning lets a composite index be split logically into smaller subindexes. In skip scanning, the initial column of the composite index is not specified in the query. In other words, it is skipped. --skip scan 让组合索引(composite index)逻辑的split 成几个子索引。如果在在查询时,第一个列没有指定,就跳过它。 The number of logical subindexes is determined by the number of distinct values in the initial column. Skip scanning is advantageous if there are few distinct values in the leading column of the composite index and many distinct values in the nonleading key of the index. -- 建议将distinct 值小的列作为组合索引的引导列,即第一列。 Consider, for example, a table employees (sex, employee_id, address) with a composite index on (sex, employee_id). Splitting this composite index would result in two logical subindexes, one for M and one for F. For this example, suppose you have the following index data: ('F',98) ('F',100) ('F',102) ('F',104) ('M',101) ('M',103) ('M',105) The index is split logically into the following two subindexes: (1)The first subindex has the keys with the value F. (2)The second subindex has the keys with the value M. Figure 13-2 Index Skip Scan Illustration The column sex is skipped in the following query: SELECT * FROM employees WHERE employee_id = 101; A complete scan of the index is not performed, but the subindex with the value F is searched first, followed by a search of the subindex with the value M. 测试: 创建表: SQL> create table dave_test as select owner,object_id,object_type,created from dba_objects; Table created. 创建组合索引 SQL> create index idx_dave_test_com on dave_test(owner,object_id,object_type); Index created. --收集表的统计信息 SQL> exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','DAVE_TEST'); PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. SQL> set autot traceonly exp; 指定组合索引的所有字段时,使用Index range scan: SQL> select * from dave_test where owner='SYS' and object_id=20 and object_type='TABLE'; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 418973243 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost ( -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 27 | 2 | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| DAVE_TEST | 1 | 27 | 2 |* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_DAVE_TEST_COM | 1 | | 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 2 - access("OWNER"='SYS' AND "OBJECT_ID"=20 AND "OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE') 指定组合索引的2个字段时,使用的还是index range scan: SQL> select * from dave_test where owner='SYS' and object_id=20; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 418973243 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost ( -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 27 | 3 | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| DAVE_TEST | 1 | 27 | 3 |* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | IDX_DAVE_TEST_COM | 1 | | 2 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 2 - access("OWNER"='SYS' AND "OBJECT_ID"=20) 指定组合索引的引导列,即第一个列时,不走索引,走全表扫描 SQL> select * from dave_test where owner='SYS'; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 1539627441 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 23567 | 621K| 52 (4)| 00:00:01 | |* 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| DAVE_TEST | 23567 | 621K| 52 (4)| 00:00:01 | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 1 - filter("OWNER"='SYS') 指定组合索引的非引导列,使用Index skip scan: SQL> select * from dave_test where object_id=20 and object_type='TABLE'; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 3446962311 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost ( -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 27 | 22 | 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| DAVE_TEST | 1 | 27 | 22 |* 2 | INDEX SKIP SCAN | IDX_DAVE_TEST_COM | 1 | | 21 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 2 - access("OBJECT_ID"=20 AND "OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE') filter("OBJECT_ID"=20 AND "OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE') 指定组合索引的最后一列,不走索引,走全表扫描 SQL> select * from dave_test where object_type='TABLE'; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 1539627441 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1774 | 47898 | 52 (4)| 00:00:01 | |* 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| DAVE_TEST | 1774 | 47898 | 52 (4)| 00:00:01 | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 1 - filter("OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE') 指定组合索引的头尾2列,不走索引: SQL> select * from dave_test where owner='SYS' and object_type='TABLE'; Execution Plan ---------------------------------------------------------- Plan hash value: 1539627441 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 830 | 22410 | 52 (4)| 00:00:01 | |* 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| DAVE_TEST | 830 | 22410 | 52 (4)| 00:00:01 | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 1 - filter("OBJECT_TYPE"='TABLE' AND "OWNER"='SYS') 通过以上测试,和之前官网的说明,Index skip scan 仅是在组合索引的引导列,即第一列没有指定,并且非引导列指定的情况下。 联合索引选择性更高咯,所占空间应当是比单独索引要少,因为叶节点节省了重复的rowid,当然branch节点可能稍微多一点。 禁用skip scan: alter system set “_optimizer_skip_scan_enabled” = false scope=spfile;
(b) 在组合索引上,只使用部分列进行查询,导致查询出多行。
(c) 对非唯一索引列上进行的任何查询。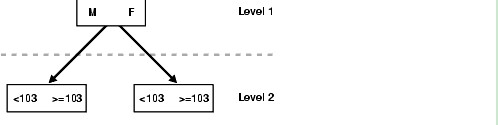
发表评论
-
DDL语句为什么不能回滚
2015-01-29 15:10 581在Sqlserver或一些其他的 ... -
EXPDP 占用的POOL理解
2015-01-29 13:33 513As of Oracle Database 10g rele ... -
Oracle Index Clustering Factor(集群因子) --转
2015-01-29 11:50 764一、本文说明: 今天在做测试的时候发现字段上有索引 ... -
关于Optimizer_index_cost_adj参数的设置(转)
2015-01-29 10:45 946关于Optimizer_index_cost_adj参数 ... -
Cursor_sharing(转)
2015-01-29 08:56 531一、Cursor_sharing简介: 这个参数是 ... -
处理上百万级记录如何提高处理查询速度
2013-10-01 17:52 5951.对查询进行优化,应� ... -
Linux 启动oracle服务
2012-01-09 09:55 851Linux 启动oracle服务 ... -
大表直接drop还是truncate后再drop
2011-12-29 13:48 10281. drop 与 Truncate操作类似的地方.drop ... -
转 DBLINK 无统计信息导致SQL变慢
2011-12-20 14:15 1116今天重庆ORACLE社区有位哥们提问,为啥索引重建(alt ... -
Oracle 性能相关的几个 视图 和 参数
2011-12-16 14:30 755一.性能视图 性能视图是Oracle中 ... -
Oracle 索引
2011-12-15 14:34 1131一.索引介绍 1.1 索引的创建语法: C ... -
Oracle Explain Plan
2011-12-14 08:54 1281如果要分析某条SQL的性能问题,通常我们要先看SQL的执行 ...






相关推荐
oracle索引类型及扫描方式大整理new
oracle索引唯一一本经典的书,讲述索引类型,索引设计。英文原版~~~
NULL 博文链接:https://stevenfeng.iteye.com/blog/1884088
主要讲解了索引的扫描方式、存储方式、索引优化等
4、索引高度:索引高度是指由于数据行的插入操作而产生的索引层数,当表中添加大量数据时,oracle将生成索引的新层次以适应加入的数据行,因此,oracle索引可能有4层,但是这只会出现在索引数中产生大量插入操作的...
Oracle 索引技术,正确使用Oracle数据库的索引不仅可以实现良好的性能,更重要的是能够创造出可伸缩的...本书在介绍各种类型索引的过程中,始终围绕性能这一主线,透彻分析了为Oracle数据库创建和优化索引的方方面面。
oracle数据库中如何建立索引,建立索引有什么优势,索引该如何使用
通过两个图形说明了在oracle数据库中b-tree索引和位图索引的工作原理
NULL 博文链接:https://hackpro.iteye.com/blog/1845366
简单示例实现如何为Oracle中sdo_geometry字段创建空间索引
总结描述Oracle 11g分区表的种类及分区索引的类型。范围分区,列表分区,散列分区,组合分区,哈希分区,全局索引,分区索引
对于oracle分区表分区索引的详细说明。 详细描述了分区表的类型,分区索引的类型 分类 。 删除或truncate 表分区时,什么样的情况索引会失效 需要重建 ,什么时候 对索引 没影响 。
本人通過實驗之後,自己的總結,教你如何選擇Oralce合适的索引类型
oracle的各种类型索引说明文件,含图解说明。希望大家看了后会有所帮助
oracle字段类型小结 CHAR固定长度字符串,最大长度2000,bytes VARCHAR2可变长度的字符串,最大长度4000,bytes,可做索引的最大长度749 NCHAR根据字符集而定的固定长度字符串,最大长度2000
VARCHAR2 可变长度的字符串 最大长度4000 bytes 可做索引的最大长度749 NCHAR 根据字符集而定的固定长度字符串 最大长度2000 bytes NVARCHAR2 根据字符集而定的可变长度字符串 最大长度4000 bytes DATE 日期(日-月-...
1)B树索引(考点):是应用最广泛的索引,也是Oracle数据库的默认索引类型。B树指的是平衡树(Balanced Tree),它是使用平衡算法来管理索引的。 适合B树索引的场合有: 表中存储的数据行数很多。 列中存储的数据的
Oracle Exception汇总(自定义Oracle异常) 使用方法举例: Exception When no_data_found then Dbms_output.put_line(‘no_data_found’); ACCESS_INTO_NULL 为对象赋值前必需初始化对象。对应ORA-06530错误。 CASE...